Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that develop on or inside an ovary. While most ovarian cysts are benign (non-cancerous) and resolve on their own, some may cause discomfort, complications, or raise concern for more serious conditions. One of the most advanced and minimally invasive surgical techniques used to diagnose and treat ovarian cysts is laparoscopy.
Understanding Ovarian Cysts
Ovarian cysts are a common finding among women of all ages, particularly during their reproductive years. Many cysts are “functional,” meaning they form as a normal part of the menstrual cycle and typically disappear within a few months. However, some cysts persist, grow larger, or become painful, prompting further evaluation and potential intervention.
What Is Laparoscopy?
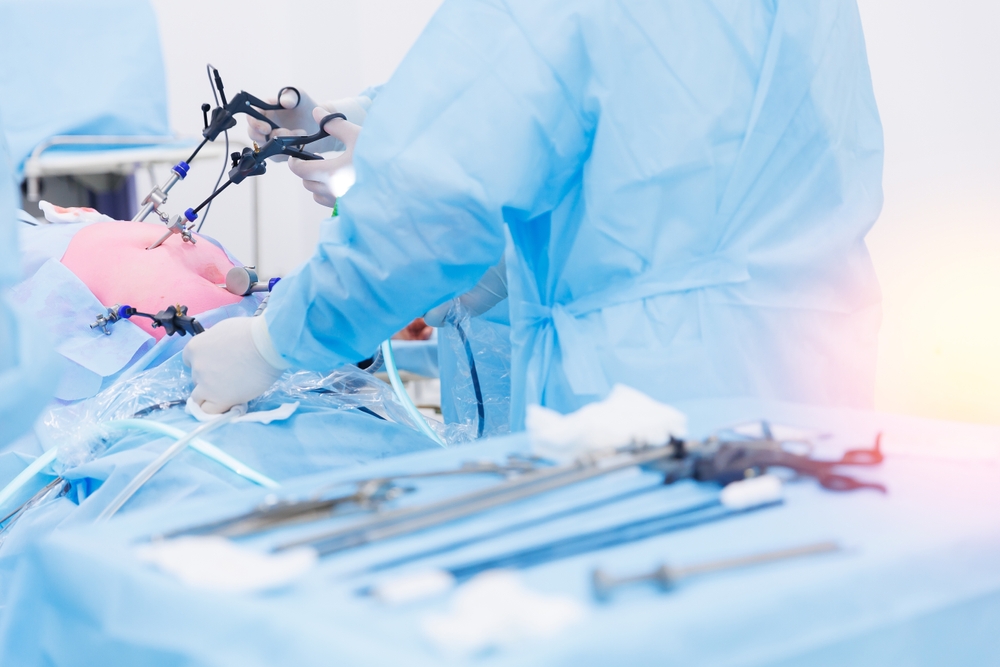
Laparoscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that uses a thin, lighted tube with a camera (a laparoscope) to view the pelvic organs. The surgeon inserts the laparoscope through small incisions in the abdomen, allowing for both diagnosis and treatment without the need for a large abdominal incision. This approach often results in faster recovery, less pain, and minimal scarring compared to traditional open surgery.
When Is Laparoscopy Recommended?
Laparoscopy may be recommended for ovarian cysts in the following scenarios:
Persistent or Large Cysts: If a cyst does not resolve after several menstrual cycles or continues to grow in size, your healthcare provider may suggest a laparoscopic procedure to remove or biopsy the cyst and confirm its nature.
Symptomatic Cysts: Cysts that cause significant pain, pressure, bloating, or other symptoms may require removal, especially if they interfere with daily activities or quality of life.
Uncertain Diagnosis: If imaging tests (such as ultrasound) cannot clearly determine the type of cyst or raise concerns about its appearance, laparoscopy provides a way to directly visualize the cyst and obtain tissue samples if needed.
Suspected Complications: Cysts that rupture, cause bleeding, or lead to ovarian torsion (twisting of the ovary) often require urgent surgical intervention, and laparoscopy is frequently the preferred approach in these cases.
Concern for Cancer: While most ovarian cysts are benign, certain features on imaging or risk factors may raise suspicion for ovarian cancer. In these cases, laparoscopy allows for careful examination and safe removal of the cyst while minimizing the risk of spreading abnormal cells.
What to Expect During and After Laparoscopy
Laparoscopy is typically performed under general anesthesia and takes about 30 minutes to an hour, depending on the complexity of the case. Most women can go home the same day. Recovery time varies, but many patients return to normal activities within a week. Your doctor will provide specific instructions and follow-up care based on your individual needs.
Contact Us to Discuss Your Treatment Options
Laparoscopy offers a safe, effective, and minimally invasive option for diagnosing and treating ovarian cysts in a variety of situations. If you’ve been diagnosed with an ovarian cyst and are concerned about your symptoms or options, don’t hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider for guidance.
If you have questions about ovarian cysts or want to learn more about laparoscopic options, contact Partners in Obstetrics & Women’s Health to schedule a consultation. Visit our office in New Lenox, Illinois, or call (815) 240-0554 today.